Support strong Canadian climate journalism for 2025
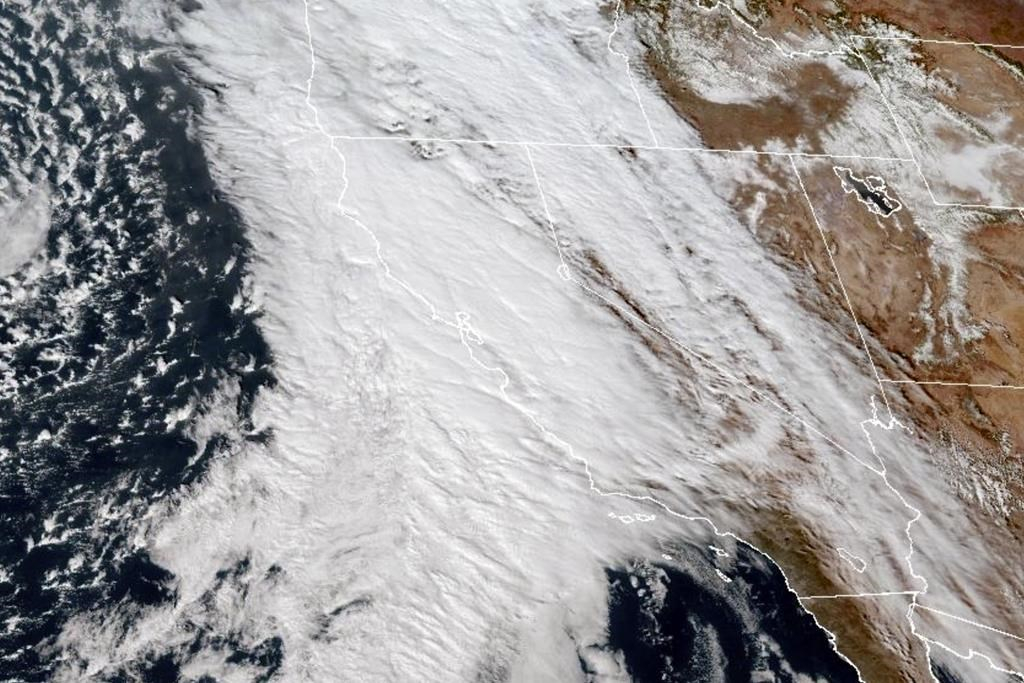
WHAT IS AN ATMOSPHERIC RIVER?
Atmospheric rivers are long and relatively narrow bands of water vapour that form over an ocean and flow through the sky, transporting much of the moisture from the tropics to northern latitudes.
They occur globally but are especially significant on the West Coast of the United States, where they create 30 per cent to 50 per cent of annual precipitation and are vital to water supplies but also can cause storms that produce flooding and mudslides, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Formed by winds associated with cyclones, atmospheric rivers typically range from 250 miles to 375 miles (400 to 600 kilometres) in width and move under the influence of other weather.
Many atmospheric river events are weak. But the powerful ones can transport extraordinary amounts of moisture. Studies have shown that they can carry seven to 15 times the average amount of water discharged daily by the Mississippi River, according to the U.S. Geological Survey.
Forty-six atmospheric rivers made landfall on the U.S. West Coast in 2023, according to the Scripps Institution of Oceanography's Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes. Nine were categorized as strong, two were extreme and one was exceptional. California experienced extensive flooding and massive snowfall.
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN AN ATMOSPHERIC RIVER REACHES LAND?
When the moisture-laden air moves over mountain ranges such as the Sierra Nevada along the California-Nevada line, the water vapour rises and cools, becoming heavy precipitation that falls as rain or snow, according to NOAA.
While traditional cold winter storms out of the North Pacific build the Sierra snowpack, atmospheric rivers tend to be warm. Snow may still fall at the highest elevations but rain usually falls on the snowpack at lower elevations. That can quickly prompt melting, runoff and flooding and decrease the snowpack needed for California's water supply.
WHAT IS A PINEAPPLE EXPRESS?
It is a nickname for a strong atmospheric river in the tropical Pacific near Hawaii.
WHERE DID THE TERM ATMOSPHERIC RIVER COME FROM?
The name came from research published in the 1990s by scientists Yong Zhu and Reginald E. Newell of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Atmospheric rivers are often referred to as ARs.




Comments