Support strong Canadian climate journalism for 2025
Approval of a nuclear waste disposal site near the Ottawa River hinged on a promise that only low-level radioactive waste would be accepted. But former nuclear industry employees and experts warn some waste slated for disposal contains unacceptably high levels of long-lived radioactive material.
The “near-surface disposal facility” at Chalk River Laboratories (CRL) will store up to one million cubic metres of current and future low-level radioactive waste inside a shallow mound about one kilometre from the river, which provides drinking water to millions of people in the region. But former employees who spent decades working at the labs in waste management and analysis say previous waste-handling practices were inadequate, imprecise and not up to modern standards. Different levels of radioactive material were mixed together, making it unacceptable to bury in the mound.
“Anything pre-2000 is anybody's guess what the hell they have on their hands,” said Gregory Csullog, a retired waste inventory specialist and former longtime employee of Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL), the Crown corporation that ran the federal government’s nuclear facilities before the Harper government privatized it in 2015.

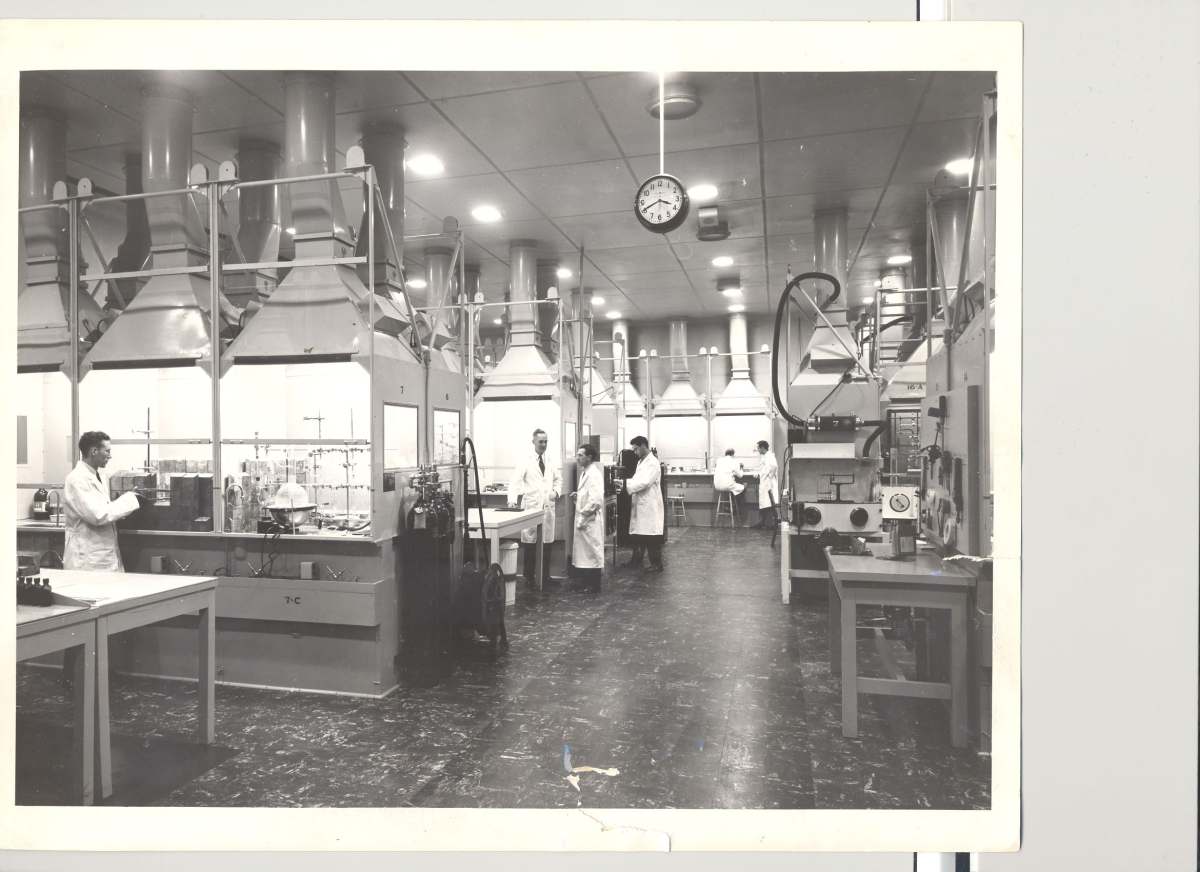
Csullog described the waste during this earlier time as an unidentifiable “mishmash” of intermediate- and low-level radioactivity because there were inadequate systems to properly label, characterize, store and track what was produced at Chalk River or shipped there from other labs. “Literally, there were no rules,” said Csullog, who was hired in 1982 to develop waste identification and tracking systems.
International safety standards state low-level radioactive waste is suitable for disposal in various facilities, ranging from near the surface to 30 metres underground, depending primarily on how long it remains radioactive. High-level waste, like used fuel rods, must be buried hundreds to thousands of metres underground in stable rock formations and remain there, effectively forever. Intermediate-level waste is somewhere in the middle and should be buried tens to hundreds of metres underground, not in near-surface disposal facilities, according to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Radioactive waste is recognized by many health authorities as cancer-causing and its longevity makes disposal a thorny issue. Even short-lived radioactive waste typically takes hundreds of years to decay to extremely low levels and some radioactive isotopes like tritium found in the waste — a byproduct of nuclear reactors — are especially hard to remove from water.
Canadian Nuclear Laboratories (CNL) originally wanted its near-surface disposal facility to take intermediate- and low-level waste when it first proposed the project in 2016. Backlash was swift and concerned groups, including Deep River town council and multiple experts, argued it would transgress international standards to put intermediate-level waste in that type of facility. In 2017, CNL changed its proposal and promised to only accept low-level waste. The announcement quelled the Deep River town council’s concern, but some citizen groups, scientists, former employees and many Algonquin Nations aren’t buying it.
CNL says its waste acceptance criteria will ensure all the waste will be low-level and comply with international and Canadian standards. Eighty seven per cent of the waste will be loose soil and debris from environmental remediation and decommissioned buildings. The other 13 per cent “will have sufficiently high radionuclide content to require use of packaging” in containers, drums or steel boxes in the disposal facility, according to CNL.
However, project opponents note that between 2016 and 2019, about 90 per cent of the intermediate-level waste inventory at federal sites was reclassified as low-level, according to data from AECL and a statement from CNL. The timing of the reclassification raised the alarm for critics, who took it to mean intermediate-level waste was inappropriately categorized as low-level so it could be stored in the Chalk River disposal facility. CNL said the 2016 estimate was based on overly “conservative assumptions” and the waste was reclassified after some legacy waste was retrieved, examined and found to be low-level.
The disposal facility will also accept waste generated over the next two decades and some shipments from hospitals and universities.
The history of Chalk River Laboratories
To fully understand the nuclear waste problem, you first have to know the history of Chalk River Lab’s operations and accidents, according to Mahdi Khelfaoui, professor of the history of energy, science and technology at the University of Quebec at Trois-Rivières and author of multiple articles on the nuclear industry and its history in Canada.

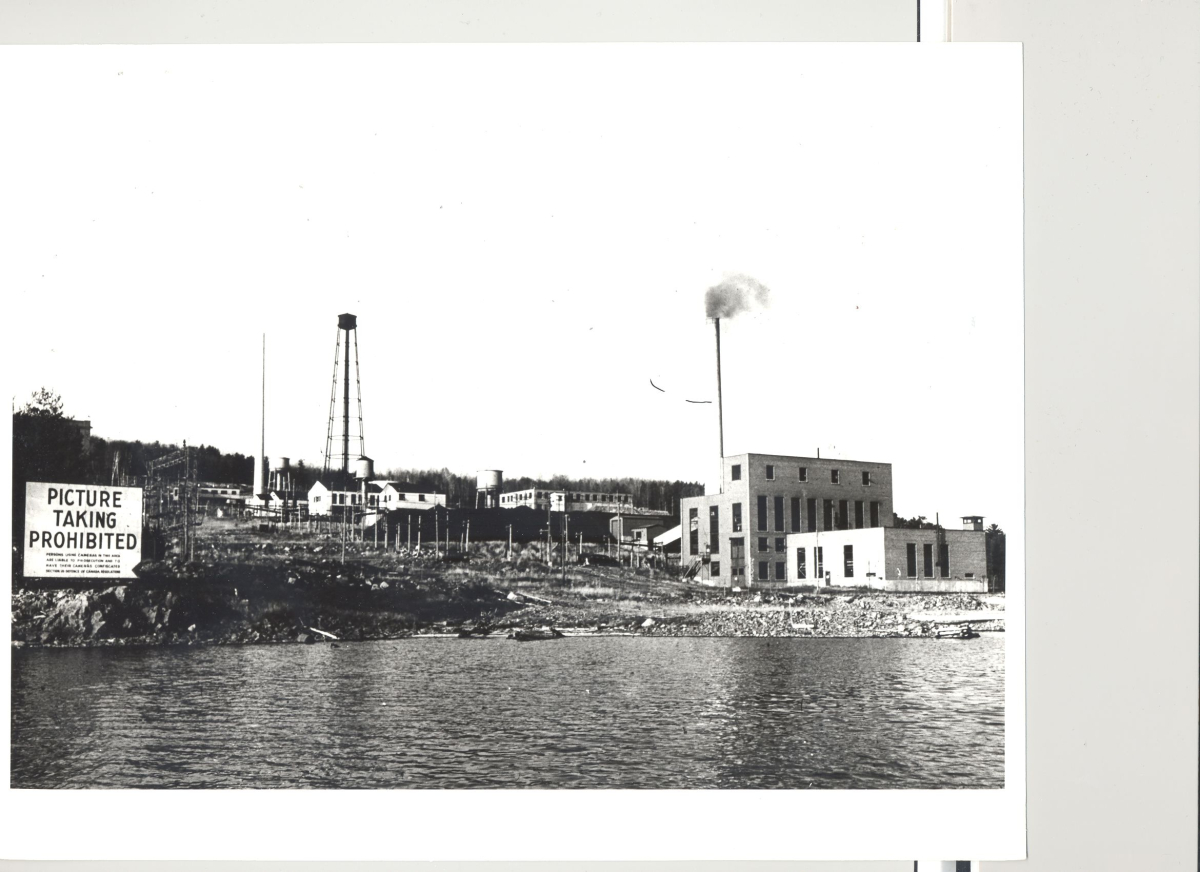
Chalk River is Canada’s biggest research facility. Built in 1944, it became home to the world’s first recorded nuclear reactor core meltdown in December 1952, followed by another incident in 1958. The 1952 accident was ranked a five on the International Atomic Energy Agency’s scale of one to seven; Chernobyl was a seven.
The partial reactor meltdown spewed radioactive material into the air and environment. During the year-long cleanup, highly radioactive debris and fuel rods were buried in a sandy area near the Ottawa River and millions of litres of contaminated water were dumped into ditches less than two kilometres from the river.
In this day and age, burying wooden boxes of fuel rods in shallow holes would be unthinkable, said Khelfaoui.
“At the time, the radioactive waste issue was almost synonymous with protecting the [commercial] interests of the nuclear industry,” said Khelfaoui. Public involvement in waste management policy was “nonexistent” before the end of the 1990s, he said.
Keeping accurate information on waste over time is a challenge and there have been inventory discrepancies at Chalk River, he added.
For example, the fuel rods buried in a “rudimentary” fashion after the 1952 meltdown were dug up and moved to safer storage in 2007, said Khelfaoui. AECL expected to find 19 fuel rods and cans in the boxes, but there were actually 32.
Over 75 years, Chalk River Laboratories developed CANDU reactors, did nuclear weapons research, supplied the United States’ nuclear weapons program with plutonium and uranium, and at one time was the world’s largest supplier of medical isotopes used to diagnose and treat cancers.

Inherent inventory issues
Until the mid-1990s, waste wasn’t even categorized as intermediate, low or high-level, said Csullog, who worked at AECL back when the Crown corporation still ran day-to-day operations at Chalk River Laboratories. Much of it was stored together in what he described as a “mishmash of unsegregated, unmarked, uncharacterized mixture of low- and intermediate-level waste.”
“This mixing and lack of identification would make all these wastes unsuitable for the near-surface disposal facility,” said Csullog.
His main concern is the packaged legacy waste, which includes contaminated protective gear, old mops, rags, tools and lab equipment from former operations. For example, some of this equipment was used to clean up highly radioactive water that leaked out of the site’s two nuclear reactors, said Csullog.
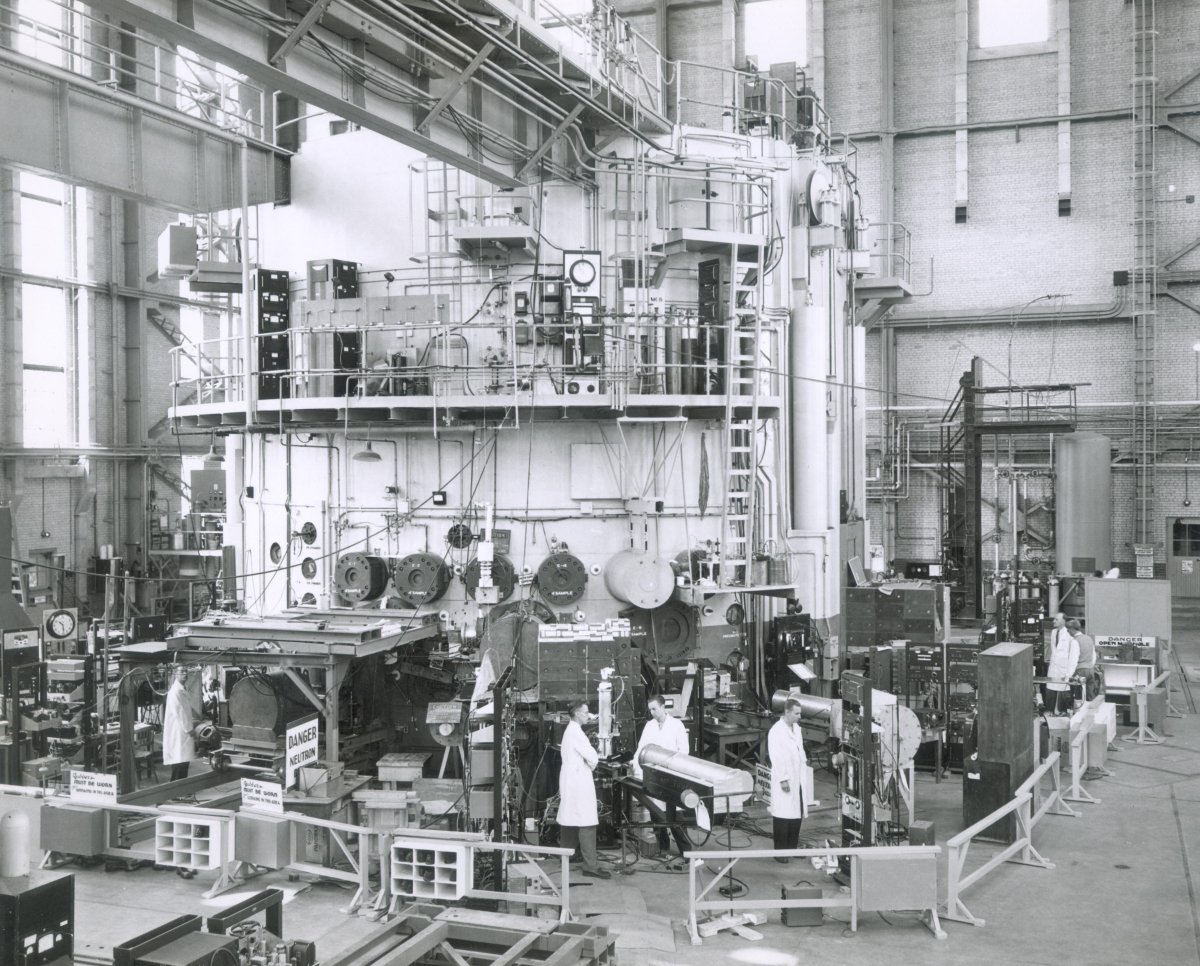
During his 21 years at AECL’s Chalk River Laboratories, Csullog developed programs to label and track all the radioactive waste created or shipped to the site. He later wrote the International Atomic Energy Agency’s guidelines on waste inventory record-keeping systems.
Developing these programs for AECL posed a challenge because many of the logbooks he was given to transcribe at the outset of his work in 1982 had precious little information on where the waste came from, how it was created or its radionuclide content. Csullog described the information in these historical records as “meaningless.” Until the mid-’90s, there weren’t even waste package labels to link waste to the correct paperwork, which also hindered his work, said Csullog.
“We didn't track it. You can't throw it all together and say, ‘We'll use historical information.’ It's irrelevant,” said Csullog.
In an email statement to Canada’s National Observer, CNL said the radioactivity of the legacy waste packages is based on records from its waste database. “CNL recognizes there are gaps” in this data and said no waste will be placed in the facility based only on historic information. Data on older legacy waste data will be reassessed and “modern analysis techniques” used to ensure there is “enough information on the waste” to make certain it meets the acceptance criteria.
The majority of packaged waste now in storage was generated pre-1995 and there is enough information to classify it as low-level waste “within a reasonable certainty,” a CNL representative told the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) during the licensing process. All waste generators have to submit documents detailing the properties of the waste and then it's up to CNL to verify the waste matches the documentation before it goes into the disposal facility.
Even after Csullog’s waste identification and tracking program was implemented in the mid-’90s, some waste with higher radioactivity was still compacted with really low-level material when it should have been kept separate, said Csullog. This was done so the radiation emitted by each bale was limited enough for people to handle and move them but in hindsight, was a mistake, he said. At this period in time, the industry was on a learning curve when it came to waste management, said Csullog.
It takes a “very, very small amount of a contaminant that's long-lived” to make low-level waste transition to intermediate, Csullog emphasized.
By the time Csullog left the Crown corporation in 1999, his final iteration of a waste inventory database was being used for package labelling, validation, inspection and compliance monitoring. While it was a vast improvement on past practices, the program still relied on estimates of waste characteristics and only helped keep tabs on newly created wastes — not the pre-2000’s waste Csullog says is unacceptable for the facility. Estimates are not a substitute for the more involved process of characterization, a process to verify the specific type and concentrations of radionuclides, said Csullog, but it helps identify which waste should be a priority and make a plan to verify its characteristics. Radionuclides are radioactive atoms.
To safely manage, dispose and store waste, it must first be characterized so you know how long the radionuclides take to decay and can then accurately classify waste as low or intermediate level based on their disposal requirements, said Kerry Burns, an expert on radioactive waste characterization methods who worked at AECL for 25 years and the IAEA for eight years.
In either case, Csullog said when he returned to AECL in 2006 after a stint working for the IAEA, his program that estimated waste characteristics and tracked them had been “abandoned.” The outstanding question in Csullog’s mind is what has been done to take its place.
In a detailed submission to the CNSC, Csullog outlined the many problems with waste identification and inventory systems during his time at AECL and the persistent lack of data to verify the radionuclide content of this older waste.
Csullog emphasized he is not against the disposal facility as a whole. He is against CNL putting this particular legacy waste into it. Instead, CNL should put this legacy waste into a deeper facility designed for intermediate-level waste since it will have to dispose of other intermediate-level waste anyway, he said.
A majority of the waste planned for disposal in the near-surface facility is soil and debris from decommissioned buildings. Most of the buildings decommissioned so far were administrative and likely had little contamination and CNL could feasibly have enough information on the radioactive properties, said Csullog. But the site’s wide range of research and development activities exposed lab equipment and some buildings to many different radioactive materials. For example, some labs separated plutonium for the U.S. weapons program, said Burns.

Because of the site’s wide-ranging activities, it is unknown exactly what concentrations of radionuclides are in the legacy waste, said Burns.
The radionuclides typically encountered at Chalk River Labs have half-lives ranging from seconds to tens of thousands of years and can give off three different types of radiation. Low-level waste should decay to extremely low levels within roughly 300 years. As radionuclides decay, some of them turn into other radionuclides with different properties, which is vital to know when you’re planning how to store waste, said Burns.
Some controlled activities — like operating a nuclear power plant — produce waste with fairly predictable types and amounts of radionuclides. As long as these predictable waste streams are kept separate, you can often measure, sample and analyze it, said Burns, who spent years at AECL developing radiochemical analysis methods to determine exact properties of waste, and authored multiple articles on these methods.
But these methods only work if the waste is consistent, monitored carefully over time and kept separate from other waste streams, said Burns.
“I am afraid that the legacy and decommissioning wastes at CNL fall into the category of a dog's breakfast,” said Burns. To know exactly how dangerous and long-lived the materials going into the facility truly are, a detailed analysis of each package and container would be required, said Burns.
According to CNL’s waste acceptance criteria, radiochemical analysis is not part of its minimum verification requirements, though it may be done as an additional verification measure.
Canada’s National Observer asked CNL which waste streams, if any, have had their radionuclide content confirmed using radiochemical analysis.
CNL said radiochemical analysis and background information are used to create “fingerprints” for waste streams based on what background information and past data exist on the waste.
“Some fingerprints have been established, while others are still in development,” said CNL. The company gave no specifics on which waste streams were examined using radiochemical analysis.
All waste will have “sufficient characterization data” to confirm it can be placed in the near-surface disposal facility, according to CNL.
Radiochemical analysis is “prohibitively expensive” and “extremely time-consuming” but is the only way to determine the inventory of long-lived, hard-to-detect radionuclides in this waste, said Burns. This chemical analysis becomes even more challenging when waste from different operations is mixed together, as Csullog and Burns said was the case for a great deal of waste pre-2000. If a sample isn’t representative of the whole waste stream, the results won’t reflect everything in it, said Burns.
Canada’s National Observer asked CNL if it has a budget or cost estimate for radiochemical analysis and which wastes will require this analysis. CNL declined to answer.
CNL is responsible for ensuring waste meets its acceptance criteria. CNL is owned by a consortium of private companies (including AtkinsRealis, formerly SNC-Lavalin). AECL receives federal funding and contracts CNL to manage and run the federal sites, including Chalk River.
Minimum requirements for verification include inspecting waste package labels and providing documents on the waste profile and management plan. CNL’s waste acceptance criteria doesn’t specify how often verification takes place. CNL declined to explain how frequently it would verify waste.

Csullog and Burns can only speak to the waste management practices from their time at Chalk River. Burns’ team at AECL used radiochemical analysis paired with another group’s measurements to characterize the mixed waste that was compacted into bales. These bales are on the lower end of radioactivity compared to other operations waste and the characterization data showed even those are unsuitable for the disposal facility, said Csullog.
CNL could have adequate systems and practices in place to characterize and track waste being generated today, they say, though neither is convinced based on the company’s submissions to the CNSC. But proper waste management today doesn’t change the fact that the Chalk River site is dealing with waste from an era when far less was known about the importance of handling radioactive waste, said Csullog.
“It was a good place to work … but when it came to waste management, it was always sort of the lowest priority,” said Burns, referring to AECL back in his day. “You're dealing with a research site where people get rewarded for publishing papers, for doing innovative research, not for handling wastes and putting it in storage.”
Natasha Bulowski / Local Journalism Initiative / Canada’s National Observer






Comments
Excellent investigative article, very informative, thank you. As a former federal government researcher, I found the last paragraph especially hit home for me. My work at the NRC did not involve toxic materials but I recognize the research culture described. The focus is on innovation and writing papers, and cleaning up the "debris" or leftover stuff from whatever experiment you were working on was a headache, something to rush through. If the same thing was happening with the research leftovers at Chalk River, but with radioactive materials, as suggested here, I can understand why this could be a big problem.
I am very concerned that the Commissioners of the CNSC do not properly understand the issues. They have the reputation of being a captured regulator, like so many others. I expect them when faced with a problem to tell people to make it go away, and not worry too much about the consequences.
Several years ago when the National Energy Board was regulating the Trans Mountain pipeline I discovered without searching
- one of the Board members had been convicted of insider trading
- one of the Board members had been appointed to the position despite a serious conflict of interest
- two Board members had met privately with a lobbyist for a fossil-fuel company
- the Board Chairman made no public objections to these.
These are all contrary to the rules for Board appointees.
If these are the standards for Board appointees in general then we need a public uprising.
Apparently all this waste could fuel SMR or Molten Salt Reactors to supply all Canadian Electricity for 5000 years. Where's the research to develop these? Nope like so much of our society just throw it away.
Can we trust private corporations not to try and dump their waste? When it is costly and time consuming to monitor them, there is always a risk of cutting corners and making mistakes. Suncor has tried to hide its spills into the Athabasca river, mining companies have a legacy of pollution and the fossil fuel industry has been allowed to use our skies as its open sewer for generations. Trust but verify. And the penalty for polluting has to be higher.
A talented young engineers career was cut short, as was his life when he was diagnosed with advanced non-Hodgkins lymphoma. At the time there was very little choice in how to combat radiation induced cancer. Not that his doctors agreed with this suggestion for the origin of his illness, and it would have made no difference to his treatment because of the dearth, at that time, of any effective treatment.
Based on the nefarious use of radioactive poisoning employed by Russia's dictator to eliminate his "enemies" it appears that radiation exposure is still a lethal event.
Simply... there is no safe level for radiation exposure. It matters not where the radiation originates; highly enriched? raw uranium wrested from the earth? or radioactive garbage, We are still playing with fire and have no tools for extinguishing those fires. However much time and effort has gone into making radiation safe we have made very little progress. I suggest that The Chalk River burial mound would be, as my husband would have opined, just a buckshee backwoods solution.